Regenerative Farming
can only be as profitable as Monocultural Farming wit our enabling Modular Autonomy Software Service. Regenerative production practices go a step beyond sustainability — they don’t just sustain the planet’s health by reducing harm, they improve that level of health. Several facts support a new regenerative trend.
40+°
Extreme temperatures of 40+°C and even 50°C are becoming increasingly frequent worldwide.
1°C
Every degree of global warming is projected to cause a 7% increase in extreme daily rainfall.
25%
The main goal of the Farm to Fork strategy is to boost organic production to reach 25% of the EU's agricultural land use by 2030
55%
As part of the European Green Deal, the Farm to Fork and Biodiversity Strategies together address the challenging transition of agriculture towards a net 55% reduction in GHG emissions by 2030
3x
There is a global market growth in regenerative agriculture with a tripling of the current market to $31.2 Bn in 2030, which will certainly develop in analogy to renewable energies due to the climate crisis.
€ 10 Bn
Farm to Fork -> € 10 Bn on research and innovation on food, natural resources, agriculture, the environment, tech and nature-based solutions for agri-food, funded by Horizon Europe.
Our Vision
We want to promote regenerative and organic agriculture through AI and robotics in harmony with nature and people. Nature Robots is developing the leading AI and robotics platform for the regenerative agriculture of the future. Thanks to Nature Robots’ modular software services, regenerative agriculture can be just as profitable as conventional monoculture agriculture. Nature Robots is a deep-tech EXIST transfer of research spin-off of the German Research Centre for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI) and is in the implementation phase of the software platform for international key manufacturers in the rapidly growing market of autonomous agriculture.
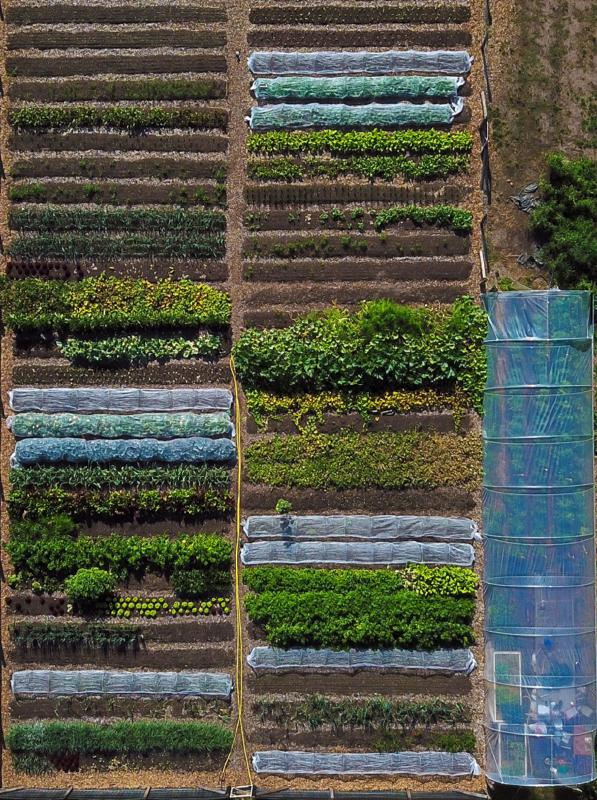


Biodiversity. Sustainability. Microfarming.
Biointensive cultivation goes beyond the cultivation of over 30 different vegetable varieties; it also has a positive impact on nature by facilitating symbiotic relationships between plants and insects. Proper soil preparation is also a critical component- compost, for example, plays a significant role in the necessary build-up of humus. Maintaining and promoting soil fertility is essential for successful biointensive cultivation. In fact, with this sustainable farming practice, a farm can operate profitably on less than one hectare of land. Despite its numerous benefits, however, many potentially interested parties lack the necessary agronomic knowledge to start their own farms.

No-till farming, biodiverse polycultures, soil conservation, mulch, anti-erosion barriers; use of compost, biofertilizers, organic bio-controllers; holistic livestock management; and edible forests. Key activities identified are Agroforestry Systems, Market Gardening, Agri-Photovoltaics, Food Forests.

SDG 2 - Zero Hunger
Regenerative agriculture improves soil fertility and water storage capacity, leading to more stable and higher yields. This contributes to food security by increasing the availability and accessibility of nutritious food. Autonomous agricultural robots can accelerate and optimize these processes by enabling precise and efficient farming methods that maximize yields and minimize losses.
SDG 3 - Good Health and Well-being
Eliminating chemical fertilizers and pesticides in regenerative agriculture reduces residues in food, leading to a healthier diet. At the same time, the environmental impact of these chemicals is reduced, which has positive effects on general health. Autonomous agricultural robots can help to further minimize the use of such agents by controlling weeds and pests in a targeted and mechanical way.

SDG 8 - Decent Work and Economic Growth
The use of agricultural robots can increase the efficiency of agricultural work and at the same time reduce the physical strain on farmers. This can lead to farmers being able to invest in more innovative and strategic aspects of their business. In addition, the development, maintenance and operation of these technologies will create new jobs and economic opportunities, particularly in the field of high technology and robotics.

SDG 12 - Responsible Consumption and Production
Regenerative agriculture promotes the responsible use of natural resources by using methods such as crop rotation, cover cropping and reduced tillage. These practices improve resource efficiency and reduce waste. Autonomous agricultural robots can optimize the use of water, fertilizers and other inputs through precise control and monitoring, leading to more sustainable production.

SDG 13 - Climate Action
Regenerative agriculture contributes to soil carbon sequestration, which helps to reduce greenhouse gases and combat climate change. Autonomous agricultural robots can support these efforts by maximizing the efficiency of carbon sequestration measures and minimizing the use of fossil fuels. By reducing tillage and promoting agroforestry, the carbon content in the soil is increased, which contributes to climate stabilization.

SDG 15 - Life on Land
Regenerative agriculture supports the conservation and restoration of terrestrial ecosystems through practices that promote soil fertility and biodiversity. This includes methods such as agroforestry and reduced tillage. Autonomous agricultural robots can support these processes through precise measures, for example by avoiding soil compaction and maintaining soil structure. This promotes habitat diversity and protects habitats for various plant and animal species.













